Square QR codes now seem to be popping up everywhere. You cannot go to a restaurant today and NOT see these images on placards, stickers, and even receipts. As popular as they are now, they have actually been around for quite some time. The COVID-19 pandemic has relaunched this phenomenon and QR codes are likely to be around for many years.
The blog post will discuss exactly WHAT makes QR codes so versatile, WHY they have become mainstream in the US, and HOW companies can implement them without forsaking users’ privacy.
Let’s start from the beginning, what is a QR code?
QR Code Vs. Linear Barcode
Linear barcodes, such as UPC barcodes, are symbols that typically contain numeric or alphanumeric data adhering to some identification guidelines. The technology to “read” or scan a linear barcode is based on reflectance properties contrasting dark bars on a light background. Light-based readers beam a red laser over the symbol to decode the barcode data so the corresponding information can be obtained from a database.
The QR code (Quick Response Code) is a two-dimensional symbol that can contain a wider range of encoded data. Unlike linear barcodes which contain information accessed in some data tables, QR codes normally encode the actual information, ranging from web address to mapping coordinates. The scanning technology used for QR codes is camera-based. Consequently, QR codes can be decoded by scanning vertically and horizontally and do not require the orientation positioning required of linear barcodes. The scanners are literally taking a picture of the QR code and that is why today’s smartphones are automatically equipped with QR code scanning technology.
History of the QR Code
The QR code was created in Japan back in 1994. Its original use was for vehicle tracking and high-speed component scanning in the automobile industry. With the introduction of the iPhone and other smartphones, QR codes began to pop up around the globe and marketers began using them for encoding web addresses, contact cards, and map locations. In Japan, the box-shaped QR codes quickly became a fixture everywhere. In the US the adaption was a little slower. Bar Code Graphics created one of the first campaigns with an enormous QR code printed on the window of a new condominium building in Chicago.
Although we did receive a lot of global exposure for the innovative use of implementing a QR Code, the actual volume was fairly limited. At that time, iPhone and Android users were required to download 3rd party scanning apps to read QR code symbols. The popularity had a quick bump but then dropped severely.
Everything changed when the iPhone integrated QR scanning within the native camera app. Users just needed to open their camera app and aim at a QR Code and suddenly a web address icon would display for instant access. Android users could use the Google Lens app for a similar user experience. By enabling instant and easy access reading these symbols, QR codes were essentially given a new breath of life.
Businesses of all types began having better luck having consumers scan on-pack and poster QR codes. The SmartLabel program was created for consumer packaged goods as a way to enable brands to provide rich data to their consumers. Our partner, the US ISBN Agency, also successfully began offering author’s QR codes linking to their book title information in their global databases.
And then the COVID-19 global pandemic happened…..
In the spring of 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic forced businesses to re-evaluate how they interacted with others. QR codes proved to be an ideal tool to facilitate contact-free interaction. As businesses, particularly restaurants, reopened, QR codes became the new instant solution for consumer information exchange. In October of 2020, Bar Code Graphics launched a very popular contact tracing and visitor sign-in service called Prvent (www.prvent.io).
Today, consumers across the globe are continually becoming more familiar with how easy QR codes are to use and comfortable relying on the data provided. There are now many solutions using QR codes.
Common Uses for QR Codes
- Menus and instruction forms
- Visitor Check-in (www.prvent.io)
- Mobile payment applications to make transactions
- QR codes on product packaging contains detailed product information
- Event or travel tickets include QR codes to authorize or log entry
- Invitation cards help guests get the venue’s location on their phone’s maps application
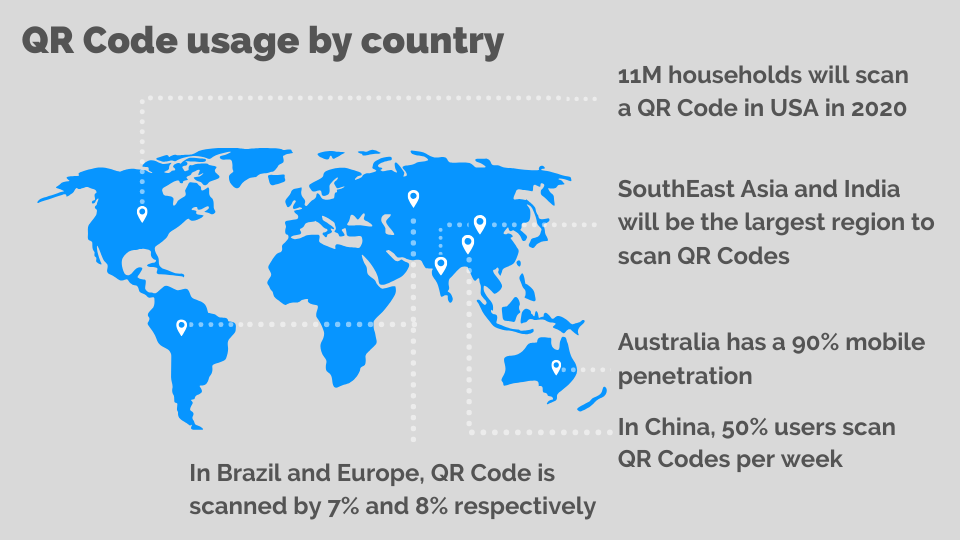
QR Code Implementation:
Easy to do it right and just as easy to do it wrong
As the US authority on barcodes and specialists on barcode creation, we have done our best to make the generation of precision barcodes (.eps files) as simple as possible. Whereas www.createbarcodes.com provides precise .eps barcode files, there are hundreds of available QR code generators for low-resolution barcodes. Regardless of which generator is used, it is important to understand the pitfalls and ramifications of poor implementation.
Static QR Codes vs. Dynamic QR Codes
A static QR code is simply one in which the target web destination is encoded directly within the symbol. Alternatively, a dynamic QR code has a re-directing URL (web address) that points to a destination web address. To reduce the length of url string and allow for smaller symbols, some QR codes point to a URL shortener, such as bit.ly. There are other QR code platforms that provide management over links and re-direction. These solutions normally track visitors and provide analytics that brands can later evaluate. The upside to these types of platforms is that destination URLs can be altered even if a QR is still out in the market. For example, a restaurant using this type of QR code platform can change the destination if menu items change.
Many small companies began creating QR code management platforms when QR codes started to become mildly mainstream in the late 2000’s. Even though the functionality of the platforms is essentially identical, the prices ranged from FREE to hundreds of dollars per month. Companies who wish to begin using QR codes need to thoroughly research their partners IF they intend on using dynamic QR codes. A small overseas company might offer competitive rates but they may be out of business in a few months. If a company printed thousands of labels or placards with the dynamic QR code and the service stopped or changed, the person scanning the QR code would go to an empty page. More importantly, there are very important privacy concerns about using 3rd party systems.
Privacy and Privileged Information
In a recent New York Times article about QR Codes, the threat of “user privacy” and “tracking” was brought up and caught the attention of many marketers. In reality, a QR code is simply a link to a web page so the user privacy concerns mirror those of just visiting a particular web page. On the other hand, some of the dynamic codes pose tracking concerns for the marketers (company using QR code). The visitor data from a 3rd party platform can all be aggregated to create connections and tracking which the marketer might now be fully aware of. Consequently, companies may want to consider using static web addresses within their QR codes and rely on Google Analytics for their own visitor tracking.
Implementation Tips:
These best practices for QR codes will yield the best results for your digital marketing strategy. However, there are a couple of simple things for you to remember not to do.
- Ensure that QR codes are accessible to your target audience
- Make sure users have the ability to scan the QR code
- Include clear instructions about what to do and expect after scanning
- Use QR code in an area with a cellular or common Wi-Fi network
- Direct traffic to a mobile-optimized landing page
These best practices for QR codes will yield the best results for your digital marketing strategy. However, there are a couple of simple things for you to remember not to do.
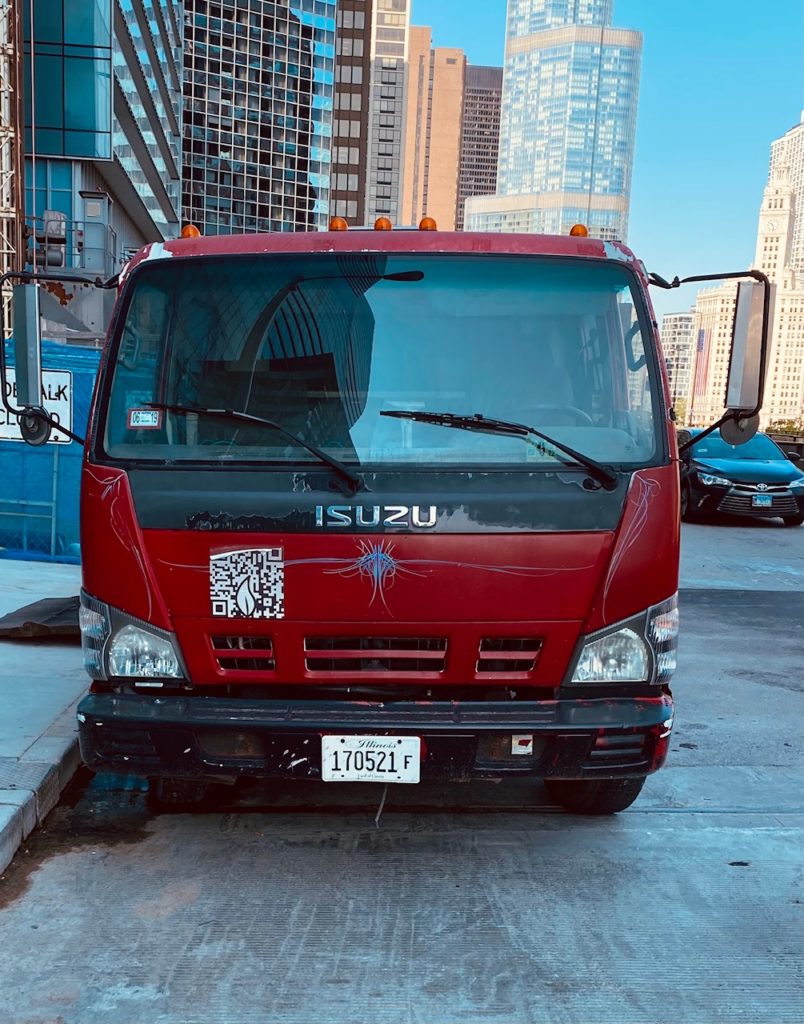
These bad practices include putting your QR code in a place with no access to mobile internet. Another aspect is the size of the QR code, the size can affect the scannability of your QR code which could seriously hinder its effectiveness. In addition, make sure you place the QR code in a place or position as not to put your potential scanners in harm’s way. As depicted below, putting a QR code on the front of a truck doesn’t seem quite right.
Anyone Can Generate a QR Code
Creating a QR code for your business or personal use is simple enough. You should figure out what you want audiences to do when using your QR code first. Have a goal and a path in mind before you decide that you need a QR code. To create a free jpg QR code files, you can go to www.createbarcodes.com. QR codes can be created 24/7 and delivered instantly.








Comments are closed.